Robotics isn’t just for sci-fi movies anymore; it’s here and it’s taking over the world—one tiny mechanical arm at a time. From vacuuming your living room to assembling your latest gadget, robots are becoming indispensable in everyday life. But before you start picturing a future filled with humanoid sidekicks, let’s dive into the basics of this fascinating field.
Basic Robotics
Basic robotics involves the study and application of robots, focusing on their design, construction, and operation. Robots function through a combination of hardware and software, enabling them to perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously. Common applications of basic robotics include household automation, where robots assist with cleaning and maintenance, and industrial settings, where robots optimize manufacturing processes.
The components of robots generally include sensors, actuators, and controllers. Sensors gather information from the environment, providing data for decision-making processes. Actuators enable movement and interaction with surroundings, while controllers process sensor input and manage the robot’s operations. For example, a vacuum robot uses sensors to navigate, ensuring it doesn’t collide with obstacles.
Basic robotics education encompasses fundamentals such as programming, electronics, and mechanics. Learning these subjects equips individuals with the skills to build and program their own robots. Schools and universities now offer courses and workshops aimed at fostering interest in the field, which has led to increased accessibility for enthusiasts.
Robotics technology continues to evolve, integrating advances like artificial intelligence and machine learning. Enhanced algorithms enable robots to improve their performance and adapt to new tasks over time. This progression opens up additional possibilities for innovation in sectors like healthcare, where robotic systems assist in surgeries and patient care.
Overall, basic robotics serves as the foundation for understanding more complex robotic systems, paving the way for developers and engineers to create smarter and more efficient machines. The growing reliance on robotics not only enhances productivity but also transforms how people interact with technology in daily life.
Key Components Of Robotics
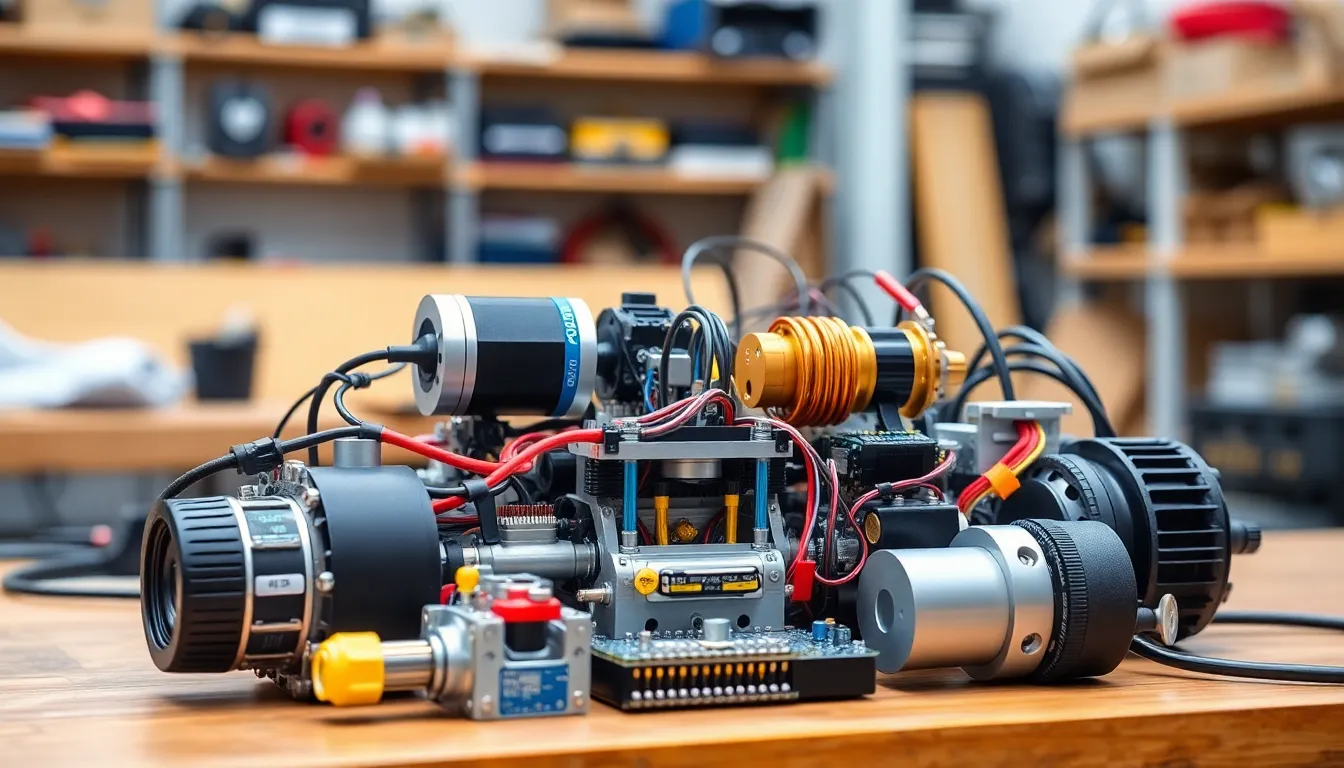
Robots integrate several key components, essential for their functionality and efficiency. Each part plays a critical role in how robots operate and interact with their environment.
Sensors
Sensors detect external conditions and provide data for decision-making. These devices measure variables like temperature, light, and distance. Infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, and cameras are common examples. Each sensor contributes unique information, enabling robots to respond to stimuli accurately. For instance, gas sensors allow robots to monitor air quality, while proximity sensors facilitate obstacle avoidance. Through this data collection, robots gain a comprehensive understanding of their surroundings, enhancing their operational capabilities.
Actuators
Actuators translate signals from controllers into physical movement within robots. These components can be electric motors, hydraulic systems, or pneumatic systems. Each actuator type possesses distinct advantages. Electric motors provide precise control, while hydraulic systems deliver high power for heavy lifting. Using actuators, robots perform various actions like gripping, lifting, and rotating. Additionally, each actuator’s response characteristics affect a robot’s speed and agility, influencing overall performance in diverse tasks.
Controllers
Controllers serve as the brain of a robotic system, processing inputs from sensors and directing actuators. Microcontrollers and single-board computers frequently act as central processing units. These devices execute algorithms that dictate robotic behavior. Programming languages like Python or C++ enhance the versatility of controllers. Through effective programming, robots can be tailored for specific applications, from industrial automation to home assistance. Controllers play a vital role in the coordination among systems, ensuring seamless operations across different robotic tasks.
Types Of Robots
Robots come in various forms, each designed to perform specific tasks across multiple domains. Understanding these types is essential in grasping the breadth of robotics applications.
Industrial Robots
Industrial robots dominate manufacturing environments, performing repetitive tasks with precision and speed. They handle tasks like welding, painting, and assembly in automotive and electronics sectors. These robots often feature articulated arms, allowing for intricate movements. Programming them involves a combination of manual coding and user-friendly interfaces. A significant benefit lies in their ability to operate around the clock, increasing productivity while reducing human error.
Service Robots
Service robots operate in roles that assist humans in daily activities. They may deliver items, provide customer service, or even perform cleaning tasks. Various industries employ them, including hospitality and healthcare. Equipped with sensors and cameras, service robots navigate environments effortlessly. For instance, hospitals use robots to transport supplies between departments, improving efficiency and minimizing cross-contamination risks. Their deployment reflects a growing trend in enhancing user experiences and optimizing service delivery.
Educational Robots
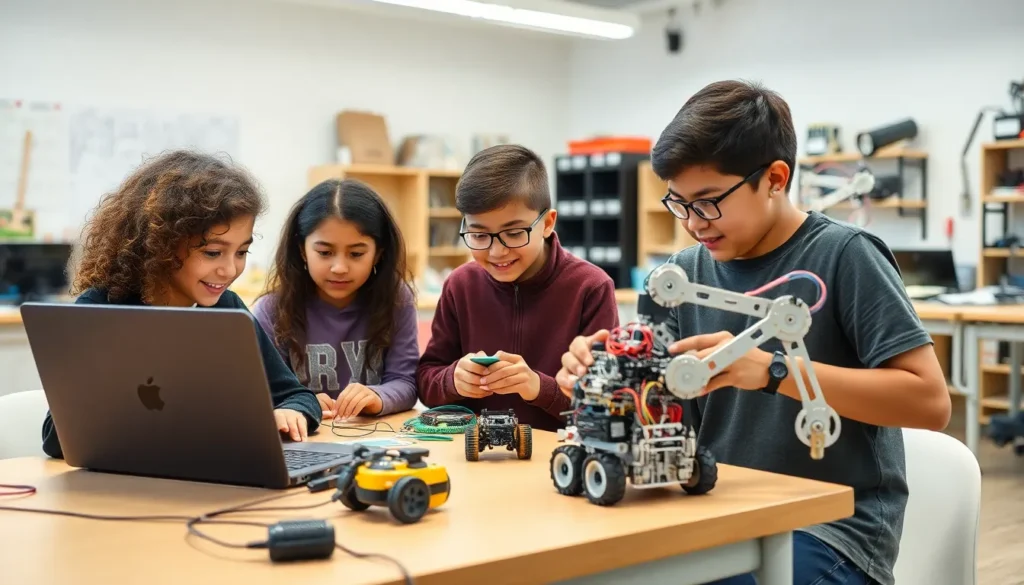
Educational robots play a crucial role in teaching programming and robotics fundamentals. They engage students in interactive learning experiences, often through hands-on activities. Schools and universities widely adopt such robots to enhance STEM education. Examples include simple robotic kits designed for beginners and advanced models for high school students. These robots enable learners to grasp concepts of mechanics, electronics, and programming. Through collaboration, students build problem-solving skills while fostering teamwork and innovation.
Applications Of Basic Robotics
Robotics applications span various industries, highlighting their versatility and impact. Each sector utilizes robots differently to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing environments rely heavily on industrial robots. These machines perform repetitive tasks, such as welding and assembly, with unmatched precision. Efficiency increases as robots operate continuously without fatigue. Safety improves when robots take on hazardous tasks traditionally handled by humans. Industries can scale production seamlessly while reducing labor costs. As technology advances, collaborative robots work alongside humans, enhancing productivity.
Healthcare
Healthcare settings benefit significantly from robotics innovations. Surgical robots assist surgeons during intricate procedures, increasing accuracy and minimizing recovery times. Rehabilitation robots help patients regain mobility through tailored exercises and real-time feedback. In addition, telepresence robots facilitate remote consultations, expanding access to medical care, especially in rural areas. These robotic applications ensure that healthcare providers deliver quality services efficiently while improving patient outcomes.
Education
Educational institutions embrace robots as teaching tools. Robotics kits engage students in hands-on learning experiences, fostering interest in STEM fields. In classrooms, students learn programming skills while building and programming robots for various tasks. Collaborative projects enhance teamwork and problem-solving abilities, preparing students for future careers. Robotics competitions motivate student participation and encourage creativity. These educational robots cultivate a new generation of innovators and technologists.
Conclusion
The world of basic robotics is rapidly evolving and becoming an integral part of daily life. From enhancing industrial efficiency to improving healthcare outcomes and enriching educational experiences, robots are shaping the future in remarkable ways. As technology advances, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning will only expand the capabilities of these machines, making them smarter and more adaptable.
Understanding the fundamentals of robotics is essential for anyone interested in the field. With increasing accessibility to educational resources, aspiring engineers and hobbyists alike can explore this exciting domain. Embracing robotics not only opens doors to innovative career paths but also empowers individuals to contribute to a technology-driven future.



